Motion in a Plane
Scalars and Vectors
- A scalar quantity is a quantity with magnitude only.
- It is specified completely by a single number, along with the proper unit.
- Examples : the distance between two points, mass of an object, the temperature of a body……etc
- Scalars can be added, subtracted, multiplied and divided just as the ordinary numbers.
- A vector quantity is a quantity that has both a magnitude and a direction and obeys the triangle law of addition or equivalently the parallelogram law of addition.
- Examples : displacement, velocity, acceleration and force…….etc.
- The magnitude of a vector is often called its absolute value.
Position and Displacement Vectors
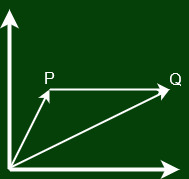
Consider a body moving in X-Y plane.
.Equality of Vectors
- Two vectors A and B are said to be equal if, and only if, they have the same magnitude and the same direction.
Multiplication of Vectors by Real numbers
- Multiplying a vector A with a positive number λ gives a vector whose magnitude is changed by the factor λ but the direction is the same as that of A :
|λ A| =λ | A| if λ > 0. - Multiplying a vector A by a negative number −λ gives another vector whose direction is opposite to the direction of A and whose magnitude is λ times |A|.
Addition of two Vectors (Graphical Method)
- Two vectors can be added, if both of them are of same nature.
- Types of vector addition are: